Issue / Details
User gets the following error when trying to get connected to a remote machine using .rdp fileERROR: The connection has been terminated because an unexpected server authentication certificate was received from the remote computer.
Related Products
Microsoft Remote Desktop, CyberArk - Privileged Access Manager (PAM, self-hosted); Privilege CloudEnvironment
What product(s), category, or business process does the requestor have? Has anything been changed recently, such as upgrades, additions, deletions?
RDS, Remote Desktop Services configured with TLS/SSL.
Cause
The underlying cause of the issue. Cause is an optional field as it is not appropriate or necessary for some types of articles.The end-user's RDP Client is configured to not allow RDP session connection on server authentication failures.
The specifics of the error is typically related to one of the following:
- Self-Signed Cert in use with RDS
- Expired Cert in use with RDS
- PSM is configured with IP (in CyberArk), and not the FQDN listed on the SAN of the RDS certificate.
- The PSM's RDS Cert CA, is not in the "Trusted Certificate" Store of the End-User's system.
Behavior change:
These types of failures use to prompt the End User with a Warning, and allow them to continue connecting through RDP. Microsoft, and other RDP Client vendors, are updating the default behavior for better security practices, and not allowing the end-user to ignore, or connect through RDP, when there is an 'unexpected' server authentication certificate received.Resolution
The answer or the steps taken to resolve the issue.3rd party vendor recommendation is to fix the underlining cause;
Correctly implementing RDP/RDS over SSL with a CA signed Certificate, that is
also trusted by the end-users system, following best security practices.
RDP
Client:
(mtsc.exe
- Remote Desktop Connection)
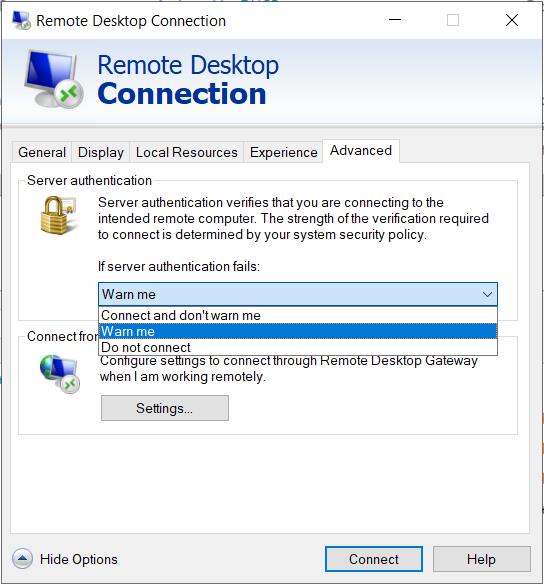
Options > Advanced > Server authentcation >
If server authentication fails:
- <Drop Down>
- Connect and don't warn me.
- Warn me
- Do not connect
RDP file:
authentication level:i:<Value>
Set the authentication level value to one of the following values:
0: If server authentication fails, connect to the computer without warning.
1: If server authentication fails, don't establish a connection
2: If server authentication fails, show a warning, and choose to connect or
refuse the connection.
Example:
to connect without warning, "authentication level:i:0".
Registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client\
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client\
*Note: if set in HKEY_CURRENT_USER; overrides HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
Variable:
AuthenticationLevelOverride
DWORD Value.
0
Type this value to configure an authentication level of "No
authentication."
1 Type this value to configure an authentication level of "Require
authentication."
2 Type this value to configure an authentication level of "Attempt
authentication."
Example
change using PowerShell:
RDP-over-SSL-server-authentication-certificate-failures

Comments
Post a Comment
What do you think?